Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
If you have purchased the [MFA] module, this feature is available. Multi-factor authentication provides enhanced identity verification by supporting a variety of login factors. Each authentication method is assigned a specific security level. When creating MFA strategies—such as User MFA, Application MFA, or User Behavior Analysis (UEBA)—you can freely configure their behavior.
User MFA
This function determines whether a user must undergo secondary authentication during login and what action to take when triggered.
⚠️ Note: If User Behavior Analysis is enabled, User MFA will be disabled and replaced by the UEBA-based mechanism.
Trigger Conditions
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Abnormal Frequency | Triggered if a user logs in repeatedly (e.g., X times within Y seconds). |
| Abnormal Network | Triggered if the login IP is not within the IPs defined in MFA - Common Settings - Network Configuration. |
| Unusual Time | Determined based on Time Settings - Restricted Hours and Trusted Zone: 1. Login during a restricted time: triggered 2. Login during allowed time: not triggered 3. Login not in any defined time and not in trusted zone: triggered |
| Unrecognized Device | Triggered if the device is not recognized as trusted. Device recognition rules are defined in Common Settings - Device Match Rules. |
| Abnormal IP | Evaluated based on IP Settings and Trusted Zone: 1. IP in greylist: triggered 2. IP in blacklist: login blocked 3. IP in whitelist: not triggered 4. IP not in any list and not in trusted zone: triggered |
| Out-of-Region Login | Triggered if the user's current city is not part of the trusted region (i.e., based on IP + account data). |
Condition Logic
You can define logical relationships between conditions when creating policies:
| Logic | Behavior |
|---|---|
| AND | All selected risks are checked. Multiple risk messages are displayed on the login page. 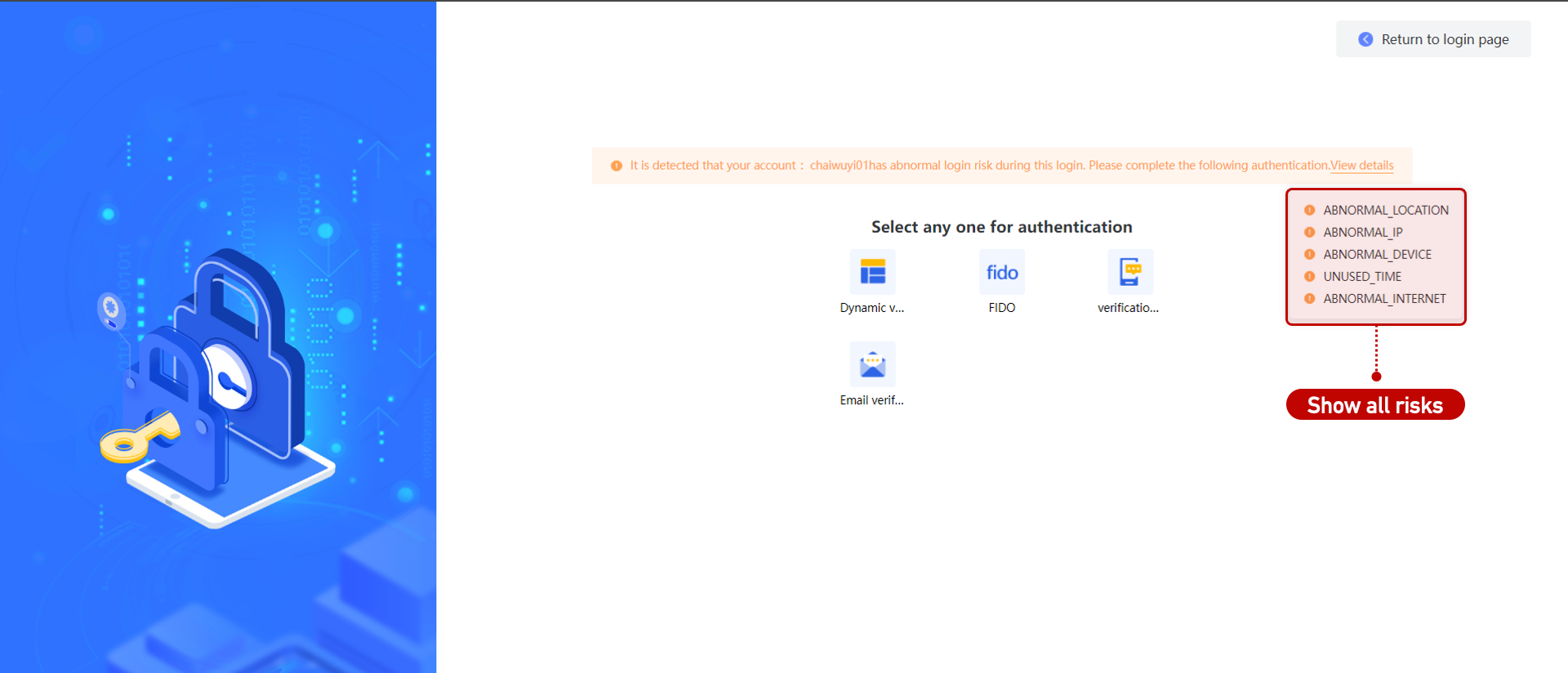 |
| OR | Risks are checked in order of priority. Once one is detected, others are skipped. Only one risk message is shown. 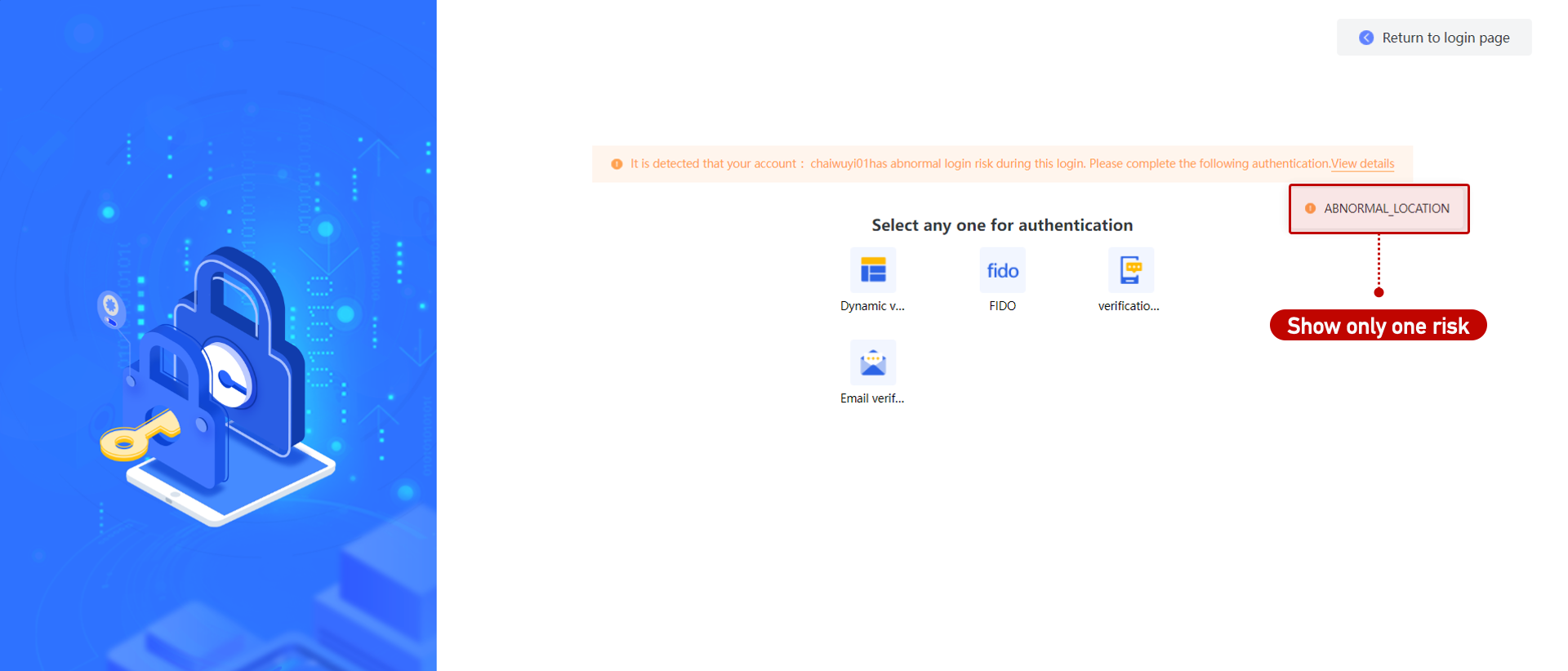 |
Authentication Action
Defines how the system should respond when login risks are detected:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Notification | Sends a risk alert to the user via SMS/email as configured in Notification. |
| No Action | Ignores the risk and allows login. |
| Block Login | Blocks login entirely. |
| Secondary Auth | Requires successful secondary authentication to proceed. |
You can also configure success/failure thresholds:
- After X successful secondary authentications within a time window, the user's context is added to the Trusted Zone, bypassing future MFA.
- After X failed attempts, the context is moved to the Quarantine Zone, resulting in login restrictions.
ℹ️ Note: A "successful" attempt includes both ignored risks and those passed via secondary authentication.
Secondary Authentication Methods
| Depth | Description |
|---|---|
| Single Method | User selects one of the configured methods for verification. |
| Auth Chain | User must complete all methods in sequence as configured. |
Priority
User MFA strategies support prioritization. The system checks if the current user matches the [Applicable Scope], then executes the strategy with the highest priority.
If the primary login method’s security level is higher than all configured secondary methods, MFA will not be triggered.
Application MFA
This feature checks whether a user needs to perform secondary authentication when accessing specific applications.
Trigger Conditions
You can specify both user scope and application scope. When a user accesses an application, the system evaluates these conditions to decide if secondary authentication is required.
Authentication Action
Once triggered, the system uses the configured authentication methods to verify the user before granting access to the application.
Priority
Application MFA supports strategy prioritization. The system evaluates the [Applicable User Scope] to determine if a user matches any strategy. If matched, it checks whether the target application is included in the strategy and then applies the strategy with the highest priority.
MFA Execution Rules:
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| No MFA Required | If the user’s primary authentication method level is higher than all MFA methods defined for the app, MFA is skipped. |
| MFA Required | If the user has already completed user-level MFA with a method whose level is higher than the app’s methods, MFA is skipped. Otherwise, the app-level MFA is enforced. |
User Behavior Analysis (UEBA)
This feature (available with the [MFA] module) provides dynamic risk detection based on user behavior. Compared with static policies, UEBA is more intelligent—analyzing IPs, network fingerprints, identity traits, time, and device characteristics to detect threats like credential stuffing, bot attacks, abnormal logins, etc.
⚠️ Note: If UEBA is enabled, User MFA is automatically disabled and all behavior risk analysis is handled through UEBA.
UEBA Configuration
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Service URL | URL of the UEBA risk evaluation API service |
| Admin Credentials | Username and password for UEBA API authentication |
Ensure that this configuration is correct for the IAM platform to use UEBA features normally.
Data Scope Configuration
Applicable to Anomalous Login Time detection. This ensures that UEBA uses a reliable dataset. If insufficient data exists for a user, and the only detected risk is "anomalous login time," the system will fall back to static user MFA handling.
Bot Detection (CAPTCHA Slider)
When UEBA detects a high bot risk score, a CAPTCHA slider can be required based on configurable thresholds.
Temporary Whitelist
Users added to this list are exempt from UEBA-based risk handling for a limited period. The exemption expires automatically after the next successful login.
Risk Trigger Conditions
UEBA assigns a risk score per scenario (e.g., abnormal IP, bot, geo-anomaly). Actions (e.g., MFA or block) are determined based on which score range the risk falls into.
Secondary Authentication Methods
| Depth | Description |
|---|---|
| Single Method | User selects one method to complete secondary authentication. |
| Auth Chain | User must pass all configured methods in sequence. |
Priority and Handling Multiple Risks
UEBA strategies can be prioritized just like static ones. The system evaluates matched strategies based on [Applicable Scope] and uses the one with the highest priority.
| Scenario | Handling Logic |
|---|---|
| One Risk Detected | The system compares the risk score to the defined threshold and takes the appropriate action. |
| Multiple Risks | 1. If any risk except "anomalous login time" requires blocking, block the login. 2. If no block, check for any MFA requirement and enforce it. 3. If only "anomalous login time" remains, fallback depends on Data Scope Configuration. |
Common Settings
These are shared configurations relevant to User MFA.
⚠️ If User Behavior Analysis is enabled, this section will be overridden by UEBA.
IP Settings
Configure IP-based allowlists (whitelists), greylists, and denylists:
| List Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Whitelist | IPs in this list are fully trusted. Logins from these IPs do not trigger any risk checks. |
| Greylist | IPs here trigger “abnormal IP” risk in User MFA. |
| Blacklist | Logins from these IPs are completely blocked. |
Network Settings
Links IP addresses to city locations. Used in MFA evaluations for Abnormal Network risk.
Three main purposes:
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| User MFA - Abnormal Network | IPs in network settings will not trigger network anomalies. |
| Trusted/Quarantine Zone Display | The displayed city name is based on this setting (or IP geolocation if missing). |
| Visualization Dashboards | Risk dashboards reflect city names based on this mapping. |
Account Settings
Configure account-based allowlists and denylists using conditions like specific users, user types, organizations, roles, etc.
| List Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Whitelist | Logins from these accounts bypass risk checks. |
| Blacklist | Logins from these accounts are completely blocked. |
Time Settings
Controls whether User MFA triggers based on login time:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Allowlist | Login during this time does not trigger "unusual time" risk. |
| Blocklist | Login during this time does trigger "unusual time" risk. |
Trusted Zone
Users are added to the Trusted Zone after a defined number of successful secondary authentications (see User MFA).
Users in the trusted zone are exempt from future MFA under the same login conditions.
You can also define expiration rules in Other - Trusted/Quarantine Expiration Settings.
| Trusted Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Device Only | All users logging in with Device A bypass “unrecognized device” risk. |
| Device + Account | Only User A using Device A bypasses that risk. |
| IP + Account | If IP is not greylisted, User A on IP 10.10.1.1 bypasses “abnormal IP” risk. |
| City + Account | User A logging in from a mapped city (e.g., Wuhan) bypasses “out-of-region” risk. |
| Time Range + Account | If login occurs during an allowed time window, User A avoids “unusual time” risk. |
Quarantine Zone
Users are added to the Quarantine Zone after exceeding a configured number of failed MFA attempts.
Logins from quarantined users are blocked if:
- Their IP is not in the whitelist
- Their account is not in the whitelist
Expiration rules can be configured in Other - Trusted/Quarantine Expiration Settings.
Login Factors
Login factors refer to the credentials used in identity authentication.
Combining multiple factors significantly enhances both identity assurance and cybersecurity.
Device Match Rules
Used in User MFA to define Unrecognized Device risk.
A device is identified using a combination of:
- Operating System
- Login IP
- Browser Type
- Device ID
This combination defines what is considered a "trusted device."
You can:
- Manually create trusted device records.
- Automatically insert them into the Trusted Zone after consistent login success.
Special Case: Device ID Enforcement
If Device ID is selected and you enable “Block login if device ID collection fails”, users must have the device plugin installed.
Otherwise, login will fail with this error:
“Device ID retrieval failed. Please enable the device ID plugin and try again.”
If a user continuously succeeds in secondary authentication (or primary login) and device info (or device + account) is included in the policy, the device will be added to the Trusted Zone.
Trusted/Quarantine Expiration Rules
When trust or quarantine entries are automatically or manually created, the expiration time is set based on this configuration.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Permanent | If unchecked, entries are valid indefinitely. |
| Timed (with interval) | If checked, entry expires at: current date + interval. |
Auto-Extend Trusted Devices
You can optionally enable auto-renewal for trusted devices.
If enabled:
When a user logs in using a trusted device or device+account during the trust period, the expiration is extended:
⚠️ Only device-related trust data (device or device+account) supports auto-extension.
Login Factors (Recap)
Login factors are identity verification credentials.
Combining two or more factors significantly improves security:
Examples:
- Something you know (password)
- Something you have (OTP token)
- Something you are (biometrics)
Summary of MFA Flow
- User MFA: Triggered during login; can be static or UEBA-based.
- Application MFA: Triggered on app access; policy-based.
- UEBA: Uses behavior analytics for dynamic risk scoring.
- Common Settings: Support trust zones, risk whitelists, device recognition.
- Device Match + Trust Expiry: Manage MFA behavior based on environment.