Application Management
The Application Management module provides flexible integration methods for enterprise applications. It supports configuring SSO with standard protocols, synchronizing data to downstream systems, customizing application types, provisioning/deprovisioning accounts, fine-grained permission control, and managing access to sensitive application resources. These capabilities help address complex enterprise integration needs.
Application Configuration
This section allows administrators to configure third-party application details such as basic information, synchronization parameters, and authentication settings. It enables users to perform SSO to target applications or synchronize user/org data to them. Additional features include application attribute mapping, account property configuration, data reclamation, and comprehensive application insights to support admin decision-making.
Initial Configuration
Application Source
Only manual application creation is supported.
Application List Configuration
Navigate to [Application Management > Application Configuration] to customize visible and searchable fields via Customization > Page List. Filtering by status, type, and protocol is supported.
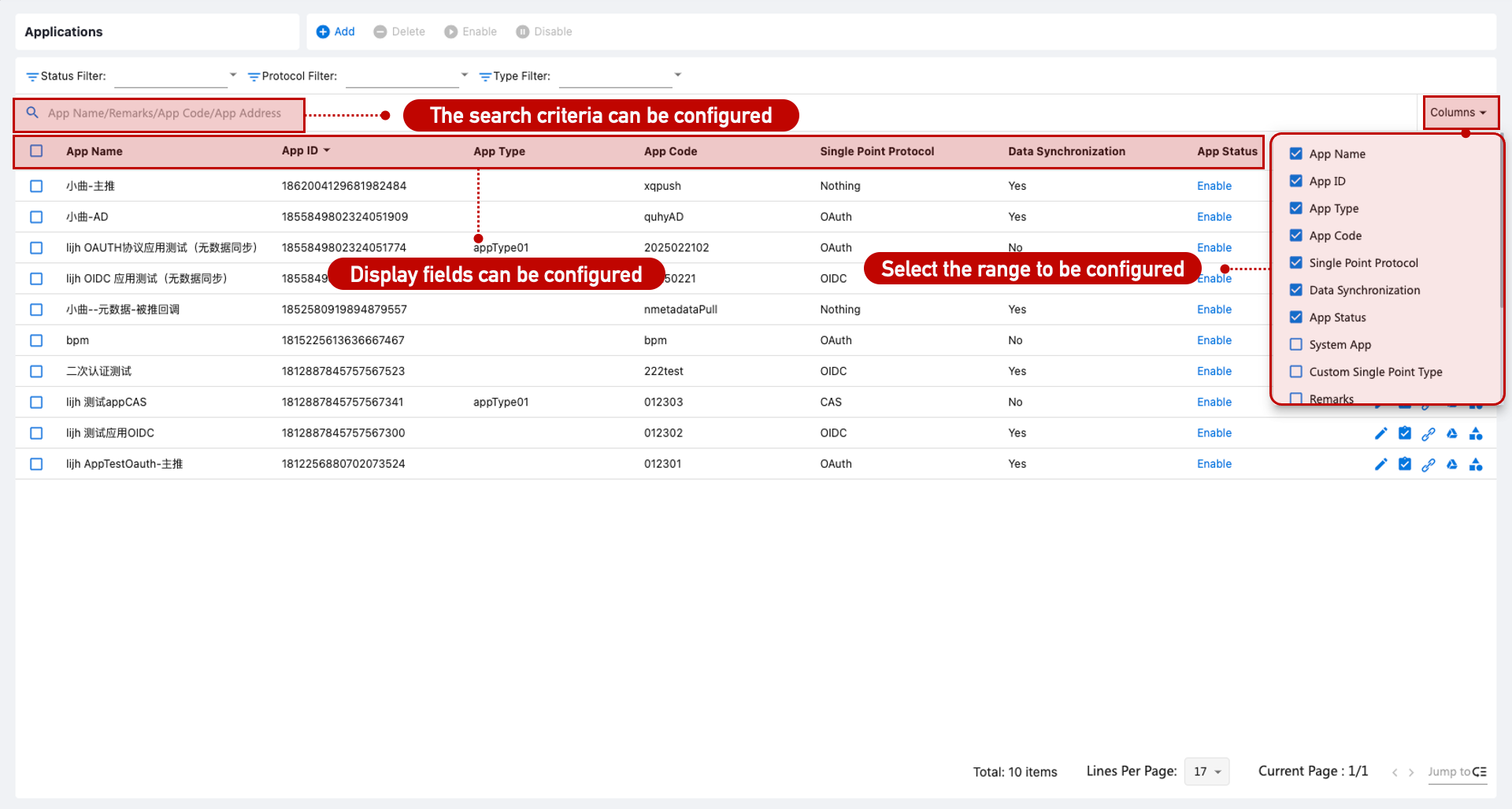
Application Form Configuration
Form customization is not supported.
Basic Application Information
| No. | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Display in Selfcare | Enabled: Application icon appears under "My Apps" in the self-service portal. If access is denied, it appears under "Available Apps". Disabled: Application icon will not appear even if the user has an account. |
| 2 | Account Strategy for SSO | - Regular: Users must have an account provisioned in IAM. - Universal: All users can log in. - Auto-provision: All users can log in; accounts are auto-created upon first login. |
| 3 | Password Algorithm | Specifies the encryption algorithm for the application's account password. |
| 4 | Application Owner | Used for approval workflows when users request account access or permissions. |
| 5 | Admin Permission Scope | Requires [IGA Module]. Defines what types of permissions admins can manage in the backend. |
| 6 | User Assignable Scope | Requires [IGA Module]. Defines what permission types users can be granted. |
| 7 | Access Request Workflow | Requires [Paraview BPM Module]. Defines the approval flow when users request access. Requires proper configuration in System Settings > Workflow Engine. |
Application Synchronization Settings
Requires [Lifecycle Management] module.
Used to synchronize IAM-managed data to the target application.
Ensure the correct plugin is uploaded via System Settings > Plugin Management. After enabling sync, select the appropriate method and plugin, then configure parameters.
Changes to application accounts will be synchronized, and user/org/position master data can be kept in sync via Authorization Center > Provisioning Policies.
Application Authentication Settings
Used for SSO integration.
Ensure a compatible plugin is uploaded via System Settings > Plugin Management. After enabling, select the SSO protocol and plugin, then configure authentication parameters.
Additional Parameters (currently unused)
| No. | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Default Browser | Specifies the browser used when users click the app icon in the portal (requires ESSO plugin). |
| 2 | Authentication Level | Derived from [Authentication Configuration > Authentication Method]. Not currently used. |
| 3 | Default Login Method | The default method when accessing the app directly. |
Field Synchronization Mapping
Requires [Lifecycle Management] module.
Configure aliases and sync flags for account, organization, and position fields. Field-level sync depends on plugin capabilities; only supported plugins allow UI-based control.
Account Field Mapping
Requires [Lifecycle Management] module.
By default:
account_no=user_uidaccount_name=user_name
Two modes:
- Simple Mode – Direct field mapping.
- Advanced Mode – Use Java-like expressions for custom logic.
Mapping Applies To:
| No. | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Account Creation | When manually creating an account, data is auto-filled based on mapping. |
| 2 | User Creation | When creating a user or provisioning per policy, account is created based on mapped fields. |
Reclamation
Requires [IGA Module].
Used to pull accounts from the target system back into IAM. Configure Identity Governance > Reclamation Policies. Supports:
| No. | Scenario | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Initialization | Reclaim existing accounts from integrated applications. |
| 2 | Identity Governance | Identify and manage unauthorized or shadow accounts by syncing downstream data to IAM. |
Application Insight
Displays detailed metadata, usage analytics, and linked accounts to assist with application monitoring and management.
Application Types
Application types (e.g., R&D, Finance, HR) allow categorization of applications for easier management and discovery. Admins select a type during app creation, and users can filter apps by type in the self-service portal.
Application Accounts
Requires [Lifecycle Management] module.
Ensure configuration is complete in Application Configuration > Synchronization Settings.
IAM provides account management for integrated applications with visibility and control over the following account types:
| No. | Account Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Orphan Account | No corresponding user in IAM. |
| 2 | Personal Account | Linked to a single user. |
| 3 | Shared Account | Linked to multiple users. |
Initial Configuration
Account Source Channels
| No. | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manual Creation | Create/import accounts via IAM admin console. |
| 2 | Reclamation Policy | Reclaim from downstream systems. Requires [IGA Module]. |
| 3 | Provisioning Policy | Auto-create based on provisioning rules. Requires [Lifecycle Module]. |
| 4 | Auto-Provisioning | If the app is configured for auto-provisioning, account is created upon first login. |
| 5 | User Request | Users apply for accounts via workflow. Requires [BPM Module]. |
| 6 | Self-Registration | Users register accounts themselves. Requires [CIAM Module]. |
Account List Configuration
Go to [Application Management > Application Accounts] and configure display/search attributes via Customization > Page List. Filtering by protocol and reclamation status is supported.
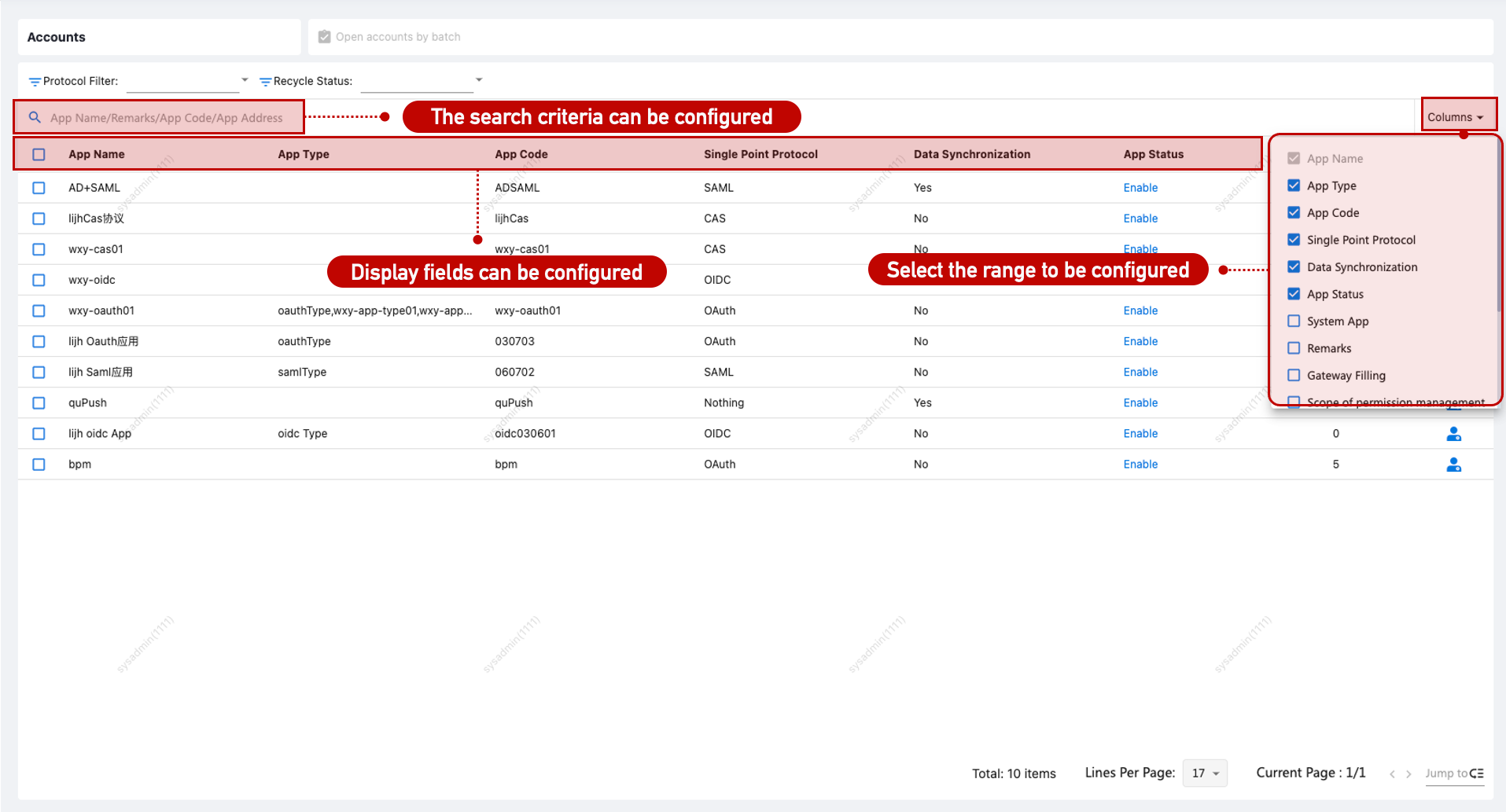
To view account details, go to [Application Management > Application Account > Details] and configure filters as needed.
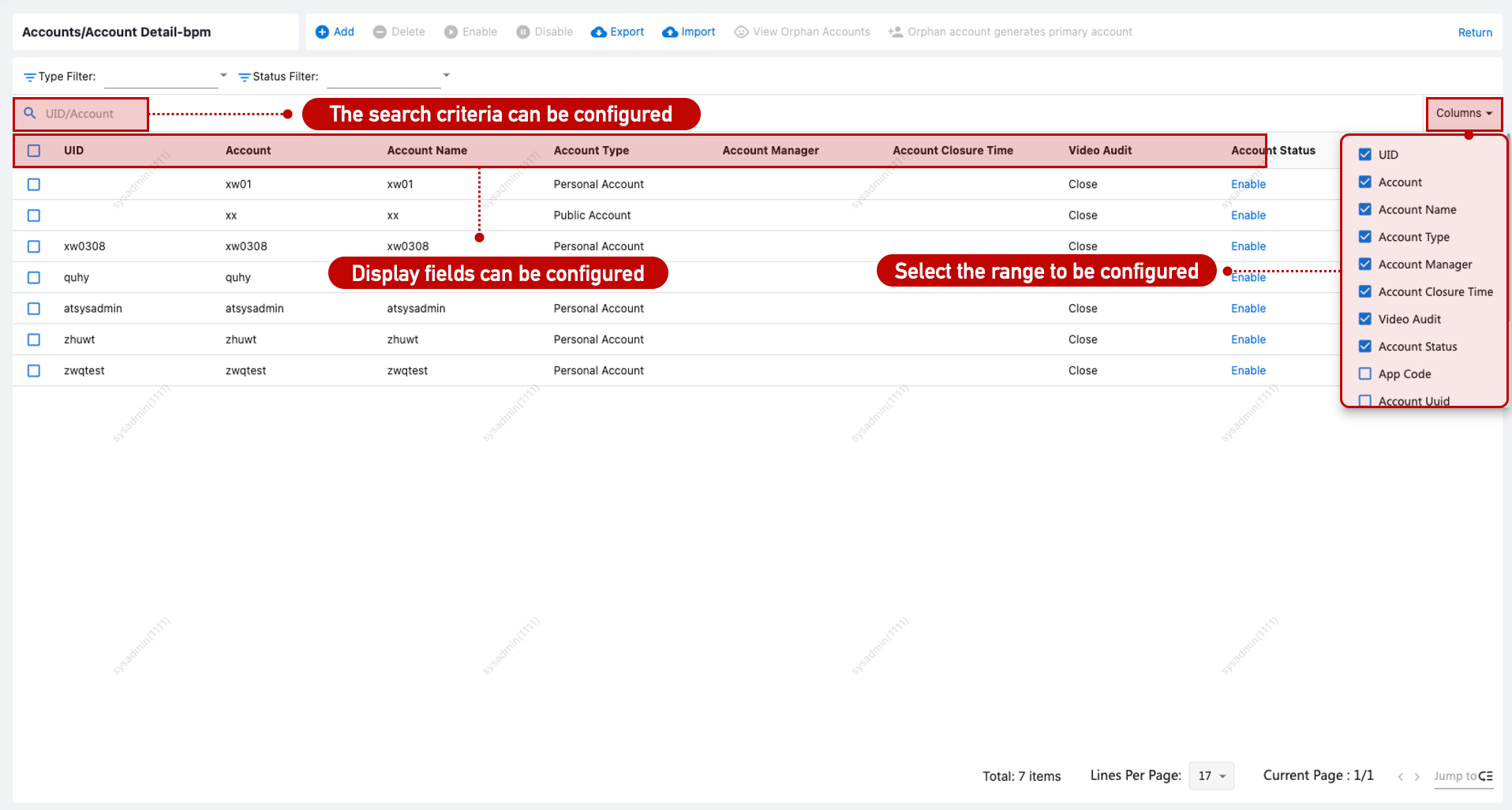
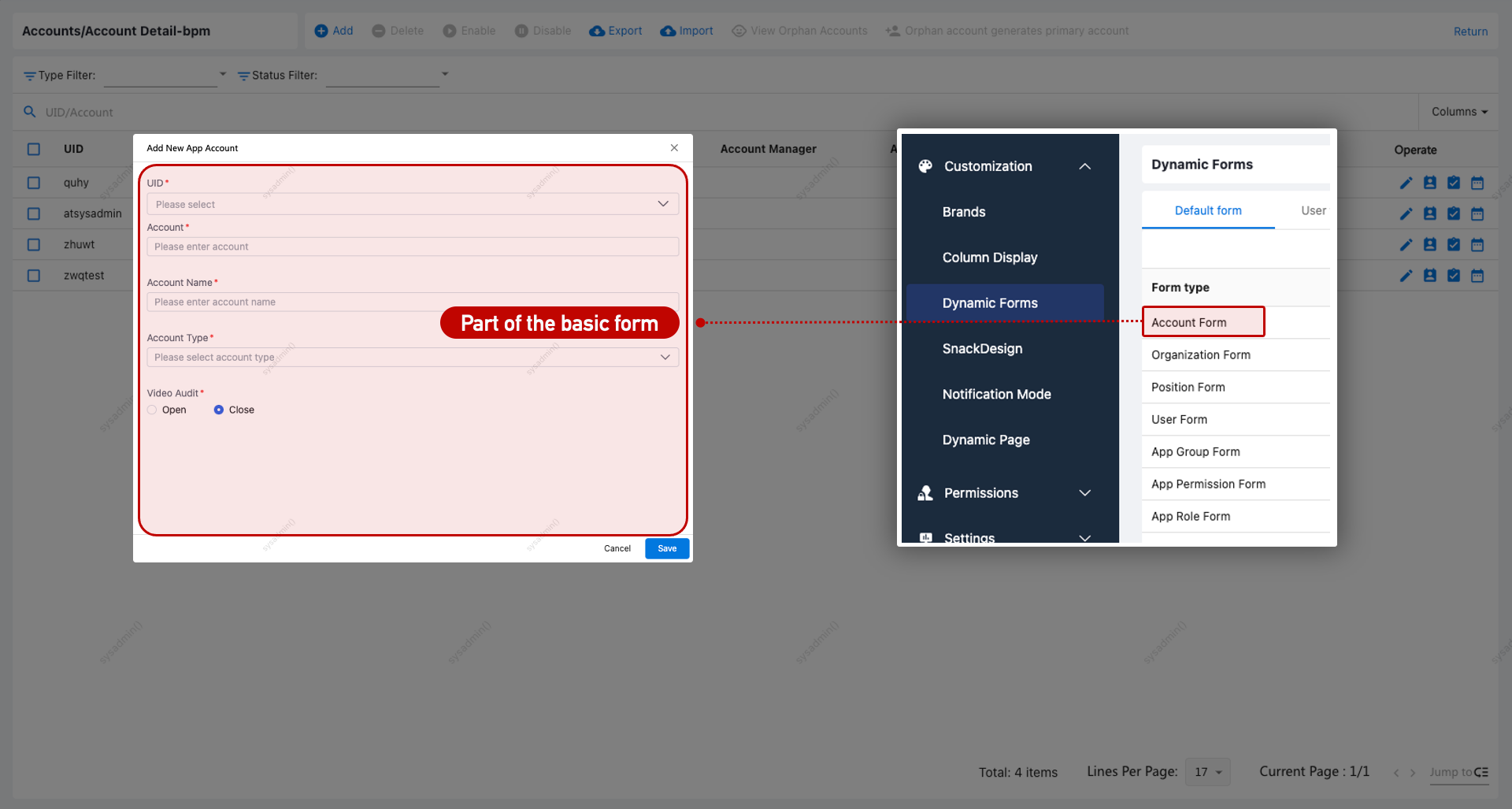
Account Form Configuration
Custom forms for accounts are supported via Customization > Dynamic Forms.
Batch Provisioning Accounts
In [Application Management > Application Accounts], select multiple applications and click Batch Provision Accounts. You can provision by organization, by user, or manually define the users.
| No. | Scenario | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | By Organization | All users under the selected organization are provisioned in selected apps. |
| 2 | By User | Selected users are provisioned in selected apps. |
| 3 | Custom Provisioning | Copy user list (e.g., from Excel), separate entries using line breaks. |
Create Application Account
Accounts can be created through the following methods:
| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manual Creation | Use Create to manually add accounts. |
| 2 | Import | Use Import to batch upload account data. |
| 3 | User Provisioning | From User Management > Permission Management, assign an account to a user. |
| 4 | Batch Provisioning | Via the Batch Provisioning process. |
| 5 | Auto-Provisioning | If the app is set to auto-provision, account is created upon first access. |
| 6 | Reclamation Policy | Reclaimed accounts are onboarded into IAM. Requires [IGA Module]. |
| 7 | Provisioning Policy | Accounts provisioned automatically per lifecycle policy. |
| 8 | User Request | Users apply for access via workflow. Requires [BPM Module]. |
| 9 | Self-Registration | Users register their own accounts. Requires [CIAM Module]. |
After selecting the user during creation, fields are auto-filled based on Account Field Mapping, with account = username, account name = full name.
Account creation supports:
| No. | Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Notification | Send notifications (email or in-app). Requires email address in user profile. See Notifications. |
| 2 | Video Audit | If enabled, session recordings are available in [Audit > Session Replay]. Requires Gateway license. |
| 3 | Data Sync | If data sync is enabled, account enters “Pending” state and is activated after sync success. |
Enable/Disable Application Account
Accounts can be enabled or disabled via:
| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manual Operation | Via Enable/Disable actions in the IAM console. |
| 2 | Provisioning Policy | Based on user status and provisioning settings. |
| 3 | Identity Governance | Auto-actions based on configured governance rules. |
Impacts:
| No. | Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Notification | Notifications can be triggered. See Notifications. |
| 2 | Login Access | Disabled accounts cannot access the app. |
| 3 | Data Sync | On enable, account enters “Pending” until successful sync to app. |
Delete Application Account
Accounts can be deleted via:
| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manual Operation | Use the Delete action in the IAM console. |
| 2 | Provisioning Policy | Deletion is triggered by user status. |
| 3 | Identity Governance | Auto-deletion via governance rules. |
Impacts:
| No. | Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Sync | Deleted account enters “Deleted” state; final removal happens after sync. |
Generate Master Account from Orphan Account
Requires [IGA Module].
For orphan accounts, you can create a corresponding IAM user by mapping key attributes, assigning an organization and position, and generating a master account in bulk.
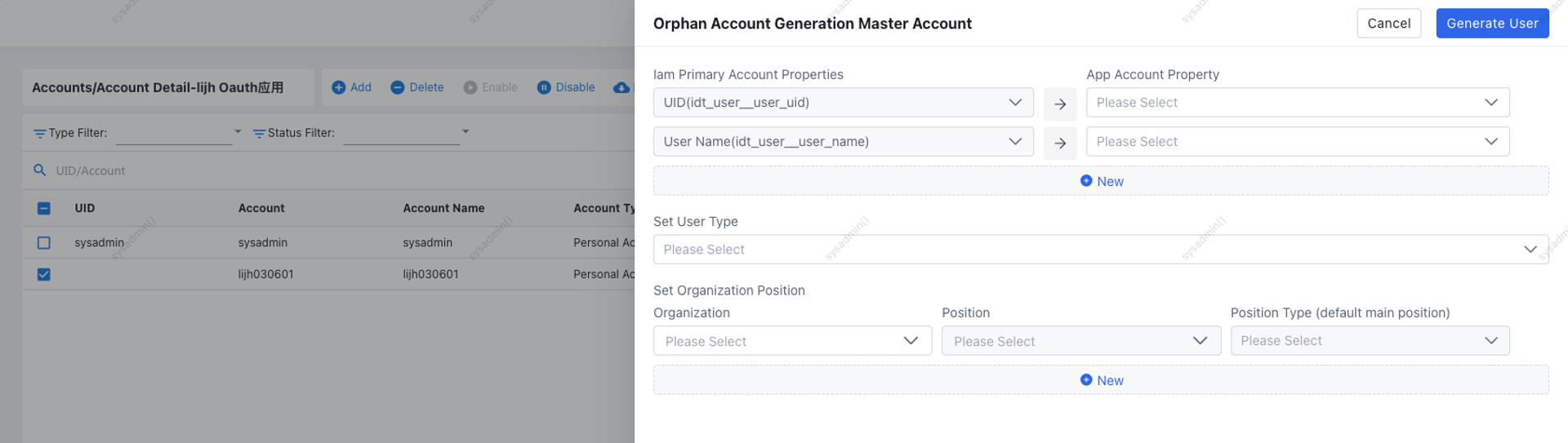
Link Master Account
Link or unlink the account from a specific IAM user.
Permission Management
Requires [IGA Module].
Allows fine-grained access control for application accounts, including permission assignments and expiration policies.
| No. | Access Path | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Direct Permissions | Directly assigned; does not include inherited or nested resources. |
| 2 | Role-based Access | Permissions inherited from assigned application roles. |
| 3 | Group-based Access | Permissions inherited from assigned application groups. |
Account Lifecycle
For personal accounts, a full audit trail is available showing the account's entire lifecycle (e.g., creation, updates, deactivation, deletion).
Application Permissions
Requires [IGA Module].
Provides fine-grained management of application permissions using multiple dimensions: resources, roles, and groups.
Initial Configuration
Permission Source
| No. | Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manual Creation | Create or import permissions via IAM admin console. |
| 2 | Reclamation Policy | Reclaim permission resources from downstream systems. Requires [IGA Module]. |
Permission List Configuration
Go to [Application Management > Application Account > Account Details], and customize visible/searchable fields via Customization > Page List.
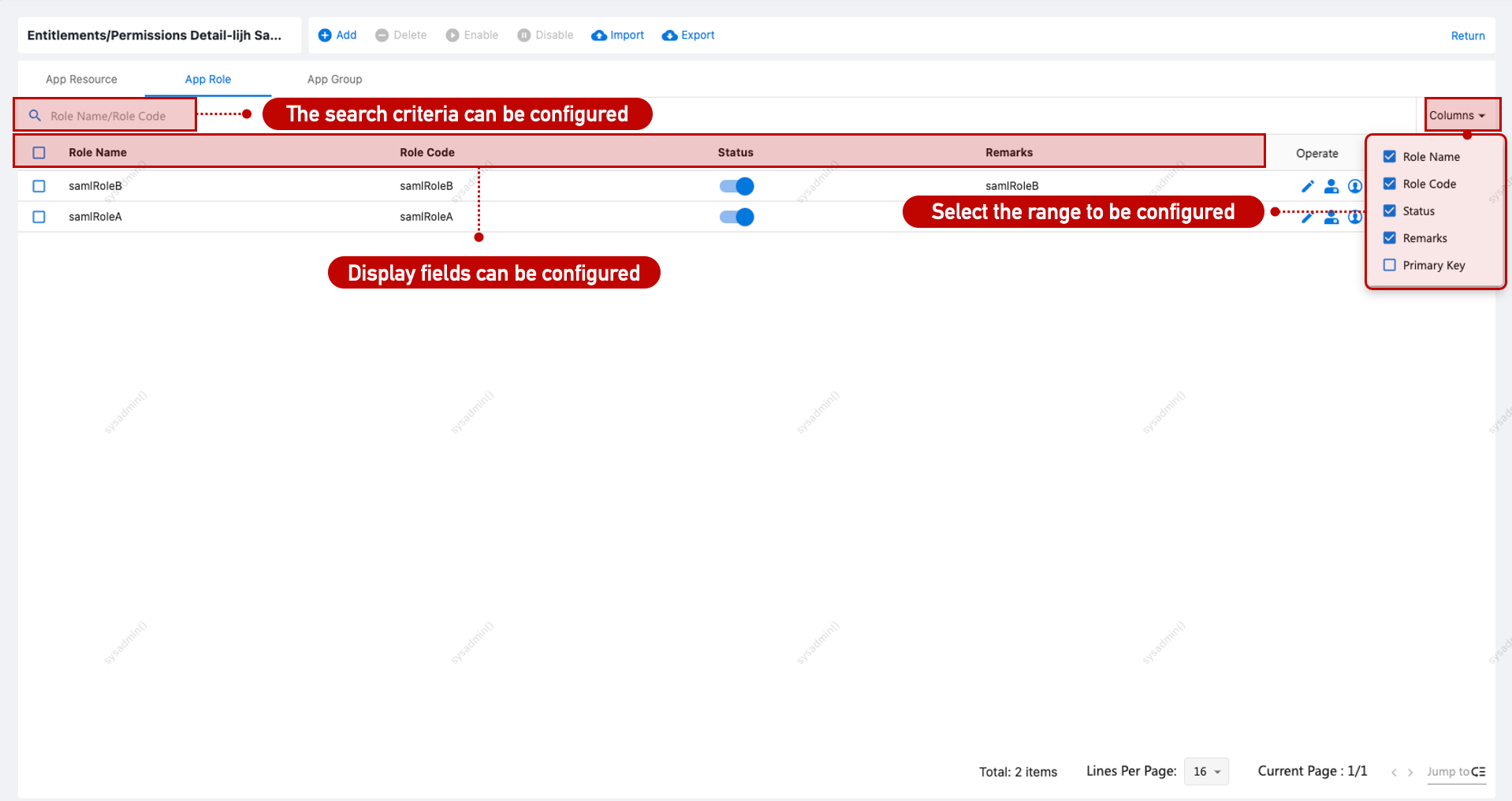
Permission Form Configuration
Application roles and groups support form configuration via Customization > Dynamic Forms.
Application resources can load different forms based on resource type. See Resource Types.
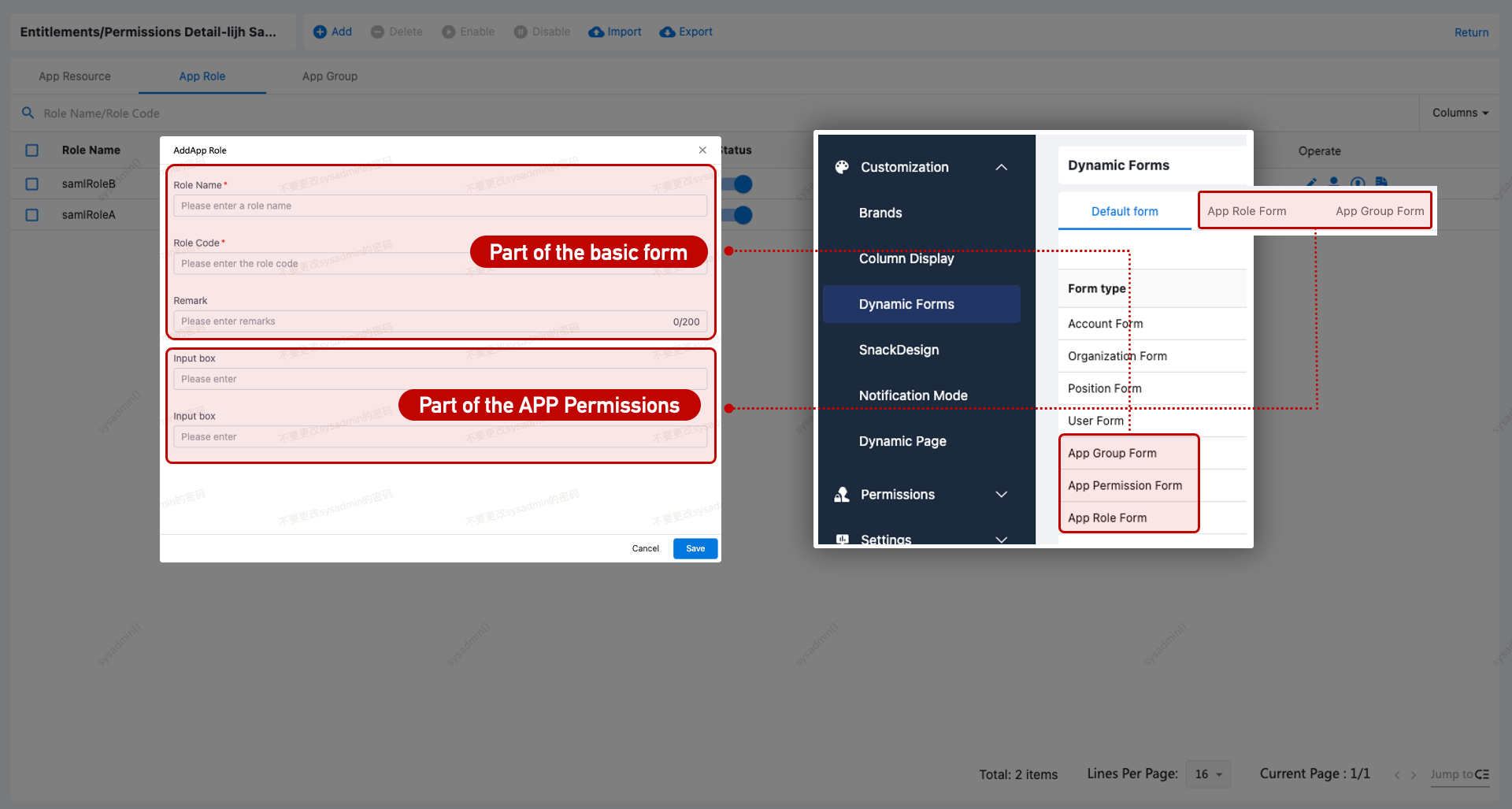
Application Resource Type Configuration
Default resource types: Menu, Function, API, Data.
To add new types:
- Go to Data Dictionary.
- Add the new type under
AppResourceEnum$Type. - Configure corresponding form in Customization > Dynamic Forms.
- Assign the resource type to the application.
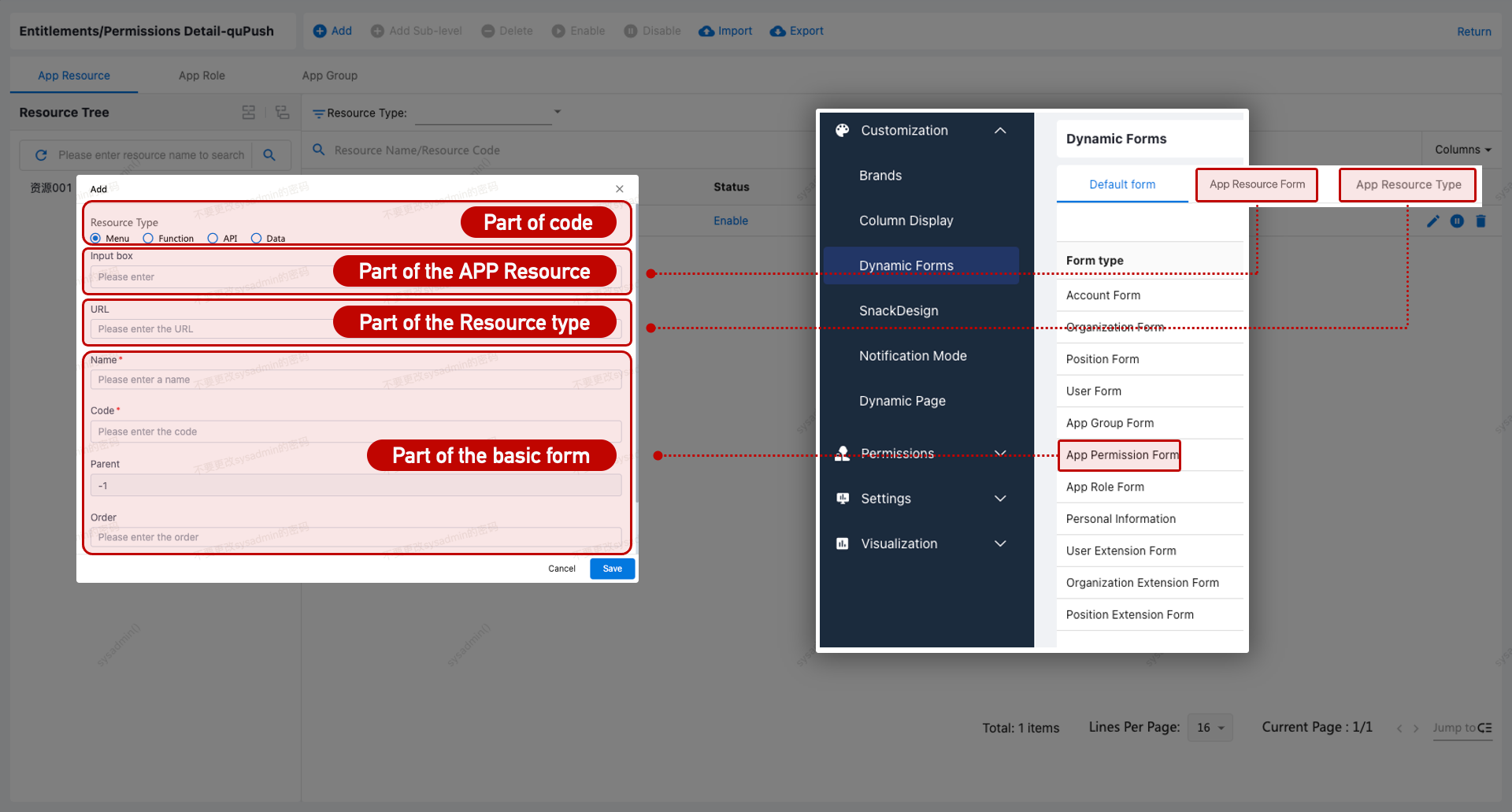
Add Permission Resource
| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manual Creation | Use Create to manually define a permission resource. |
| 2 | Import | Batch import resources. |
| 3 | Reclamation Policy | Pull resource data from integrated applications. Requires [IGA Module]. |
Sensitive Resource Management
Requires [IGA Module].
Certain applications, roles, or resources can be flagged as Sensitive to enhance security. Sensitive Resource Owners can monitor access, and revoke permissions for inappropriate use.
View Permission Details
Admins can review the access details of a sensitive resource, including linked users and roles. This view helps understand the resource's access history and allows timely remediation.